Microtubule
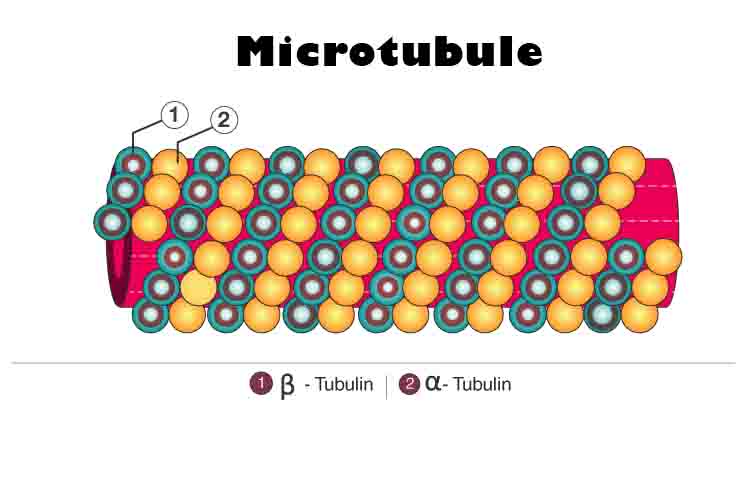
Microtubule Definition The microtubules in a cell’s cytoskeleton are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta tubulin. This cytoskeleton gives the cell shape and keeps its organelles in place by creating a network of protein filaments. A microtubule measures about 24 nanometers thick, which makes them the largest structure in the cytoskeleton. … Read more