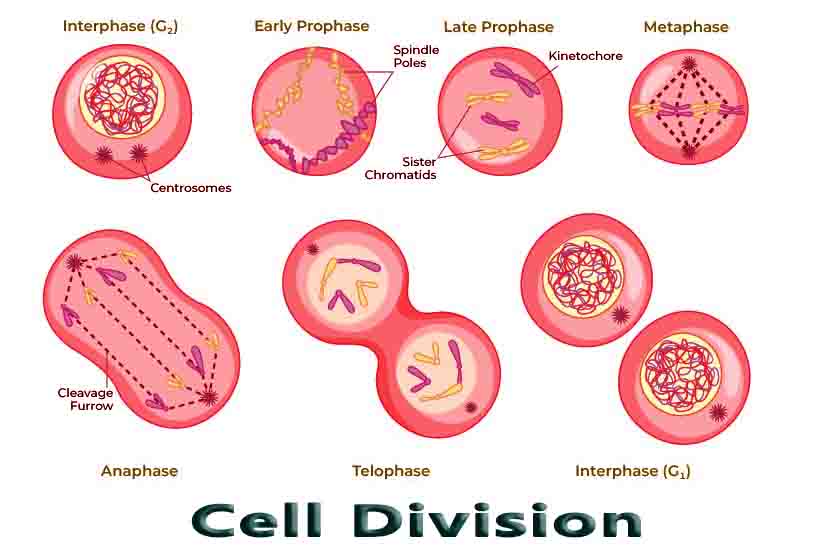
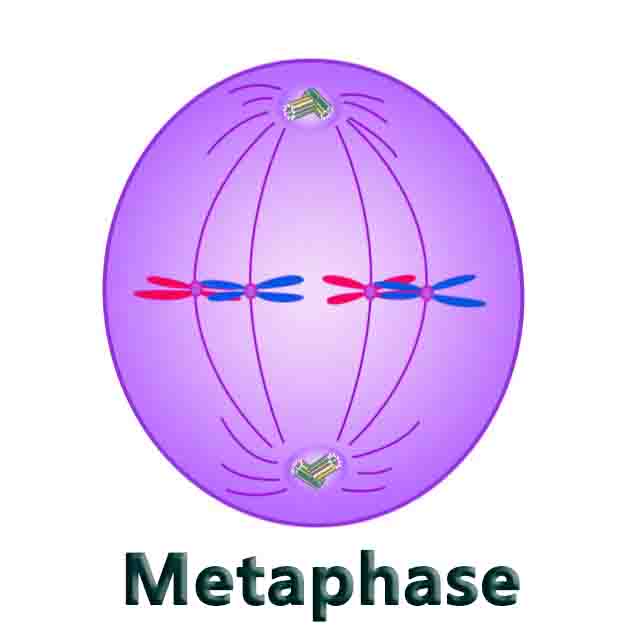
Cell Division
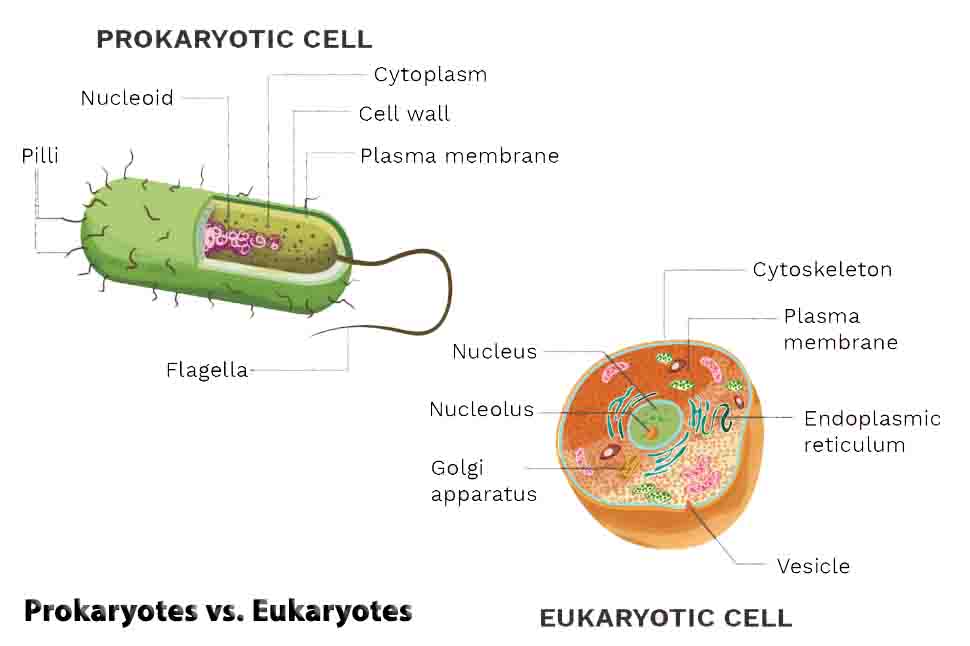
Cell Division Definition In order to divide, cells go through a process called cell division. Depending on the type of organism dividing, there are several types of cell division. Over time, organisms have evolved different and more complex ways to divide their cells. Prokaryotes, or bacteria, divide their cells by binary fission. Mitosis is used … Read more